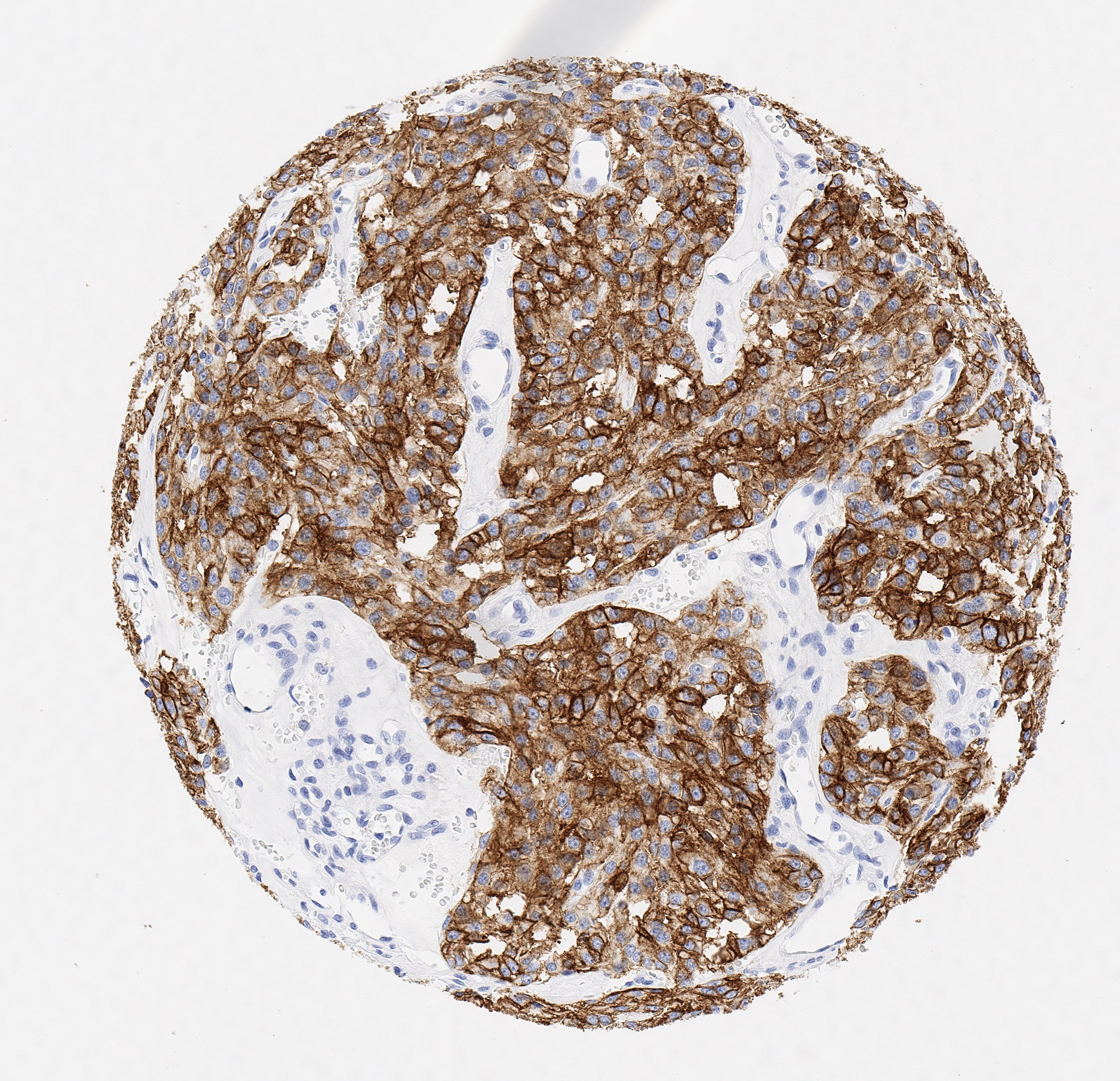
PD-L1, also known as CD274 or B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1) is highly expressed in the heart, skeletal muscle, placenta and lung and weakly expressed in the thymus, spleen, kidney and liver. PD-L1 is expressed on macrophages and activated T- and B-cells, dendritic cells, keratinocytes and monocytes. Moreover, several human cancer cells express PD-L1 at high levels. Binding of PD-L1 with its receptor PD-1 on T cells inhibits t cell proliferation and the production of cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-2. It has been shown that PD-L1 helps tumor cells to evade anti-tumor immunity and blockade of PD-L1 reduces the growth of tumors in the presence of immune cells.
PD-L1 is commonly over expressed on tumor cells or on non-transformed cells in the tumor microenvironment. PD-L1 ex-pressed on the tumor cells binds to PD-1 receptors on the activated T cells, which leads to the inhibition of the cytotoxic T cells. These deactivated T cells remain inhibited in the tumor microenvironment. PD-1 and PD-L1/PD-L2 belong to the family of immune checkpoint proteins that act as co-inhibitory factors, which can halt or limit the development of the T cell response.
Anti-PD-L1 antibody Clone JAL1 has been developed specifically for routine immunohistochemical (IHC) detection of PD-L1 in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue specimen. Moreover, JAL1 has been validated for the identification of PD-L1-positive macrophages and tumor tissues under pathological conditions.