PD-L1, auch bekannt als CD274 oder B7-Homolog 1 (B7-H1), ist in Herz, Skelettmuskel, Plazenta und Lunge besonders stark und in Thymus, Milz, Niere und Leber nur schwach exprimiert. PD-L1 wird exprimiert auf Makrophagen sowie aktivierten T- und B-Zellen, dendritischen Zellen, Keratinozyten und Monozyten. Darüber hinaus exprimieren mehrere menschliche Krebszellen PD-L1 in hohen Konzentrationen. Die Bindung von PD-L1 mit seinem Rezeptor PD-1 an T-Zellen hemmt die T-Zellproliferation und die Produktion von Zytokinen, wie z.B. Interleukin (IL)-2. PD-L1 hilft den Tumorzellen der Anti-Tumor-Immunantwort zu entgehen während die Blockade von PD-L1 den gegenteiligen Effekt hat: Das Tumorwachstum wird bei Anwesenheit der Immunzellen reduziert.
PD-L1 wird häufig auf Tumorzellen oder auf nicht-transformierten Zellen in der Tumormikroumgebung überexprimiert. PD-L1 bindet an PD-1-Rezeptoren auf aktivierten T-Zellen und führt so zur Hemmung der zytotoxischen T-Zell Antwort. Die deaktivierten T-Zellen bleiben dabei auch in der Mikroumgebung des Tumors gehemmt. PD-1 und PD-L1/PD-L2 gehören zur Familie der Immuncheckpoint-Proteine: Sie wirken als koinhibierende Faktoren, um die Entwicklung der T-Zell-Antwort zu blockieren oder einzuschränken.
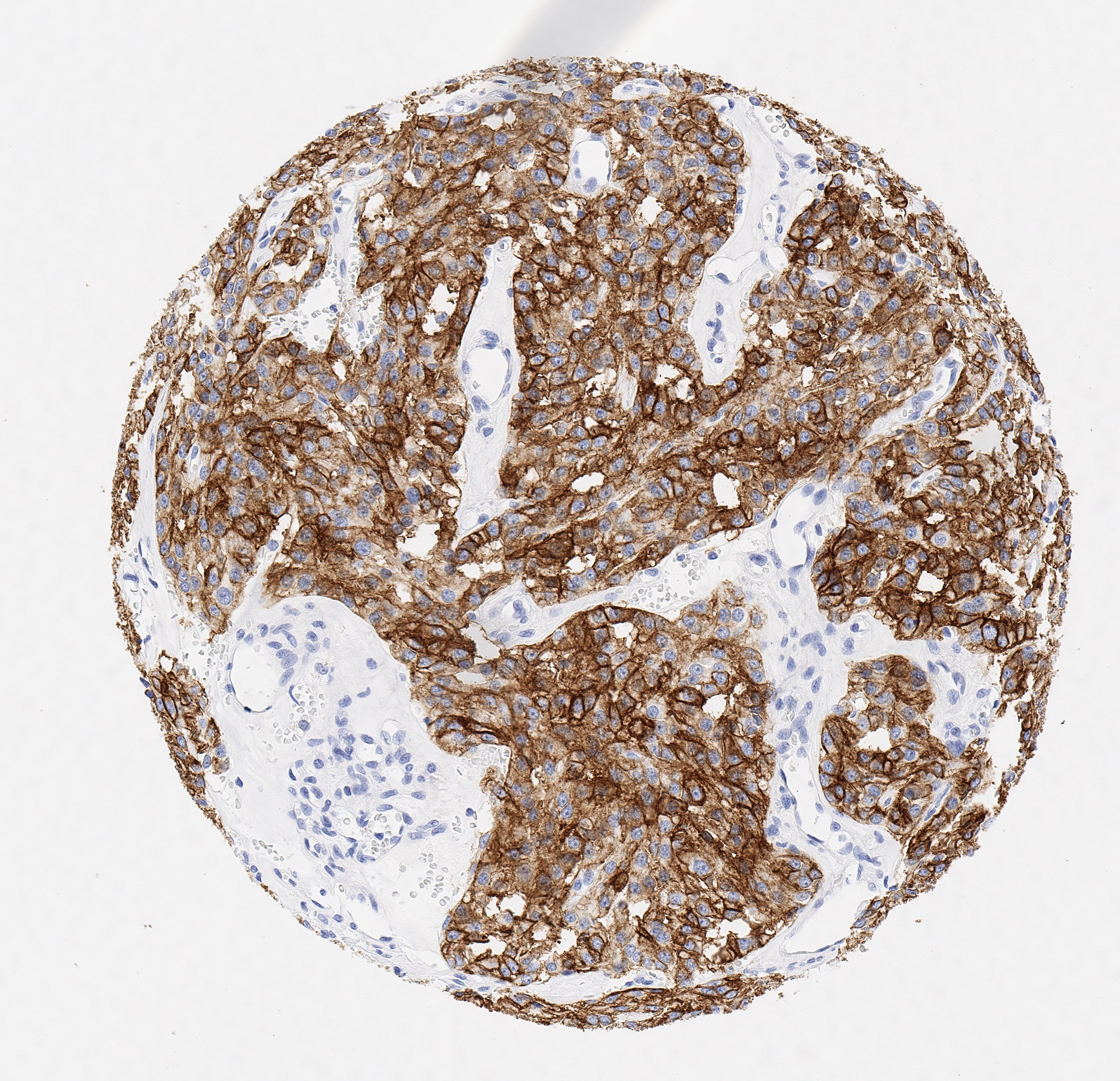
Der Anti-PD-L1-Antikörper Klon JAL1 wurde speziell für den routinemäßigen immunhistochemischen (IHC) Nachweis von PD-L1 in Formalin-fixierten, Paraffin-eingebetteten Gewebeproben entwickelt. JAL1 wurde darüber hinaus für die Identifizierung von PD-L1-positiven Makrophagen und Tumorgeweben in der Histopathologie validiert.